Porro II PrismensystemMonokulare und Ferngläser mit Porro-II-Systemen weisen eine typische Bauweise des Prismengehäuses auf: dieser ist zylindrisch und wirkt wie eine runde Dose (s. 3. Foto). |
Porro II Prism SystemMonoculars and binoculars with a porro II system have a typical construction of the prism body. It is cylindrical and looks like a round box (s. 3. photo). |

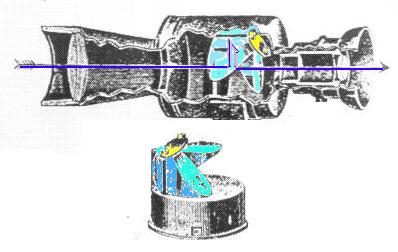

Die Konstruktionszeichnungen zeigt den Strahlengang innerhalb eines Fernglases (hier historisches Modell) und im Prismensystem (s.u.). |
The construction sketch shows the path of light within the biinocular (here a historical model) and through the prism system (s. below). The older "Ross 7x50" has the prism design from the sketch: 2 prisms cemented together (the inner ocular lens cemented to the prism); themini porro system (last picture) has three prisms combined to a porro II system. |
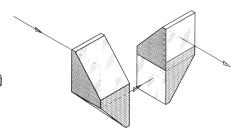


In der Prismendose werden die Prismen entweder durch einen angeschraubten Metallbügel oder direkt vom Deckel gehalten. |
The prisms are held either by a clamp or directly by the prism body cover. |


Ein weiteres Beispiel für ein Porro II-Monokular ist das Carl Zeiss 18x50, das Barr & Stroud CF41, das YM8-1 bzw. YM8-2. |
Another example of a porro II monocular is the Carl Zeiss 18x50, the Barr & Stroud CF41, the YM8-1, and the YM8-2. |
Fotos: Zeun; Schemazeichnung adaptiert aus F. Watson "Binoculars ...", S. 16f.